It’s often used to complement well-known efficiency measures that rely on the asset or equity values. Unlike these indexes, the net profit margin compares net income to total revenue. This indicator is based on the idea that each sale a company makes translates into revenue.
Calculating Service Revenue
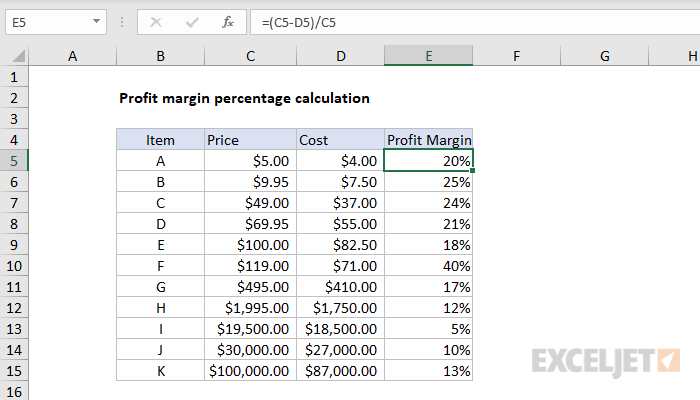
The following data has been extracted from income statement of Zain & Maria corporation. Net profit margin provides an overall picture of a company’s profitability. This is why it’s important to consider additional factors beyond net profit margin, even when making comparisons within the same industry. That said, it’s important to remember that even when comparing percentages between similar businesses, an investor must account for differences not reflected in the numbers. If your company sells services as opposed to products, the calculation is just as simple.
What Is Net Profit Margin? Formula and Examples
Such entities can improve their NP ratio only by doing some possible reduction in costs, because raising the price of their products or services would result in lost market share. These entities generally keep their focus on improving their absolute net profit number rather than the ratio value. Also, the net income margin of different enterprises varies significantly across industries. For example, information services in the U.S. reveal, on average, a fairly high net profit margin ratio of about 13.4%. At the same time, the shipbuilding industry is characterized by a negative value of this indicator, -1.8%.
- The figure can be calculated by dividing the net profit of a company by its revenue.
- Net profit (NP) ratio can be a useful tool for measuring the overall profitability and operating performance of a commercial entity.
- For example, a company with a net profit margin of 20% will keep $0.20 for every dollar generated in sales.
- A higher number usually indicates that the company is effectively managing costs, though it’s important to keep the larger context in mind.
How to Calculate Net Income Margin
By analyzing how a company’s financial results have changed over time, common size financial statements help investors spot trends that a standard financial statement may not uncover. The common size percentages help to highlight any consistency in the numbers over time–whether those trends are positive or negative. The standard figure used in the analysis of a common size income statement is total sales revenue. The common size percentages are calculated to show each line item as a percentage of the standard figure or revenue.
The denominator used is, however, the net sales which is typically the entity’s primary source of revenue. Net profit margin (also known as “return on sales”) is a profitability ratio that measures the percentage of net income to sales. Net profit margin is one of the most important indicators of a company’s financial health. By tracking increases and decreases in its net profit margin, a company can assess whether current practices are working and forecast profits based on revenues. Net profit ratio should be applied in your analysis with caution, because a low ratio may not always be a sign of bad operational performance. Entities would normally exhibit a low NP ratio when they purposely adopt an affordable or low-price strategy to grasp a larger market share.
Net income formulas can be expressed in several ways, though you can use a net income calculator to simplify the work. Allowances are price reductions that the customer initiates because of an issue with their order. That can range from problems with quality, incorrect items, or longer than expected shipping times. Let’s first illustrate the calculation of net profit ratio through a couple of examples and then proceed to its significance and interpretation. However, remember this is only one part of the picture and a more complete analysis will provide a better understanding of the company’s financial position.
Net profit is calculated by subtracting all of the company’s expenses from total revenue. Because costs are accounted for, it reveals how well a company is generating profits compared to costs. Since the net profit margin 5 5 cost-volume-profit analysis in planning managerial accounting is represented as a percentage, it’s easy to use it to compare the profitability of peers. Analysts also frequently use net profit margin to assess a company’s valuation or when constructing financial models.
A company’s net income is its gross profit minus its cost of goods sold, or COGS. In the case of service-businesses, the net income is gross profit after deducting the service cost. Rather than calculating it, you can always find net income at the bottom of the income statement. A component percentage analysis shows the relationship between specific line items on a financial statement and the total amount on the statement. For example, to calculate the net income, take the total sales and subtract expenses and taxes. To show the relationship between the line item – sales and the total amount that includes the line item – and net income, you divide net income by total sales.

Recent Comments